Nd3+ sensitized dumbbell-like upconversion nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy application†
Abstract
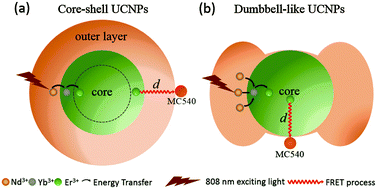
Better tissue penetration and lower overheating problems mean 808 nm near-infrared laser excited upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) have potential in bioapplications. Dumbbell-like structured NaYF4:Yb/Er@NaNdF4:Yb nanoparticles are fabricated in this work and applied in photodynamic therapy (PDT). The epitaxial growth along the c axis attributed to the large structure mismatch of NaNdF4versus NaYF4 has been demonstrated to play a key role in the growth of the dumbbell structure. Due to better space separation in this structure, energy back-transfer from Er3+ to Nd3+ is prohibited partially, and the optimized Nd3+ doping concentration is up to 90% for a high UC emission intensity. PDT effects of these dumbbell-like structured UCNPs upon 808 nm laser irradiation were examined and compared with isotropic NaYF4:Yb/Er@NaYF4:Nd0.2 core–shell and NaYF4:Yb/Er@NaYF4:Nd0.2@NaYF4 core–shell–shell UCNPs. The results show that the dumbbell-like UCNPs are most effective in generating singlet oxygen (1O2) and killing cancer cells in PDT though their UC emission intensity is lower than that of the core–shell–shell UCNPs. This research presents a simple yet valid strategy to balance the UCL efficiency and FRET efficiency, which may lead to better PDT therapeutic effect for cancer therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...