A peptide–lipid nanoparticle assembly platform with integrated functions for targeted cell delivery†
Abstract
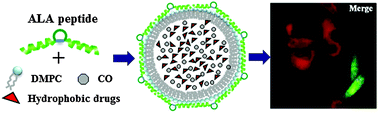
Liposomes are extensively used as drug carriers because of their biocompatibility, low toxicity, and controlled release properties, however challenges exist in the control of their particle size, surface properties and targeting functionality. In this work, we report a peptide–lipid nanoparticle platform that can achieve nanoparticle formation, surface functionalization and hydrophobic drug loading in an integrated assembly process. A designer peptide that harbors bivalent amphipathic α-helices linked by a central loop (ALA peptide) was used to encapsulate lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). The bivalency design affords higher peptide helicity and lipid-packaging efficiency, and allows encapsulated hydrophobic molecules for more stability under long-term storage. The central loop structure displays sufficient surface exposure as demonstrated by the interaction between penta-histidine installed LNPs and Ni-NTA agarose. RGD-inserted and cytotoxic iridium complex-encapsulated LNPs showed preferential entry and selective cytotoxicity to integrin high expression cancer cells, while showing reduced toxicity to non-cancer cells. Further study indicates that a constrained cyclic conformation of RGD is required to fully exert targeting capability, suggesting an intact structural exposure on the LNP surface. In summary, we demonstrate a simple yet effective method of peptide-based LNP surface modification with potential for various targeted deliveries of hydrophobic drugs.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...