A layered drug nanovehicle toward targeted cancer imaging and therapy†
Abstract
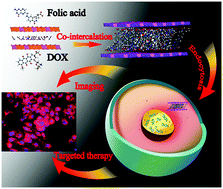
A layered drug nanovehicle was fabricated via the co-intercalation of doxorubicin (DOX) and folic acid (FA) into the gallery of layered double hydroxides (LDHs). This supermolecular nanovehicle (denoted as DOX–FA/LDH) demonstrates excellent fluorescence imaging and targeted therapy toward cancer cells. The nanovehicle shows a uniform platelet morphology with an average diameter of ∼171 nm. The unique host–guest interactions lead to a high dispersion of DOX, and in vitro tests reveal a legible and strong fluorescence imaging for the DOX–FA/LDH sample. In addition, the DOX–FA/LDH material produces a high anticancer activity toward HepG2 cells but rather low cytotoxicity to the normal cells (L02 cells), as a result of the overexpression of FA towards cancer cells. This work provides a facile approach for the design and preparation of a drug nanovehicle with significantly enhanced biocompatibility, diagnosis and targeted therapy, which can be potentially applied in medical imaging and chemotherapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...