A bodipy based fluorescent probe for evaluating and identifying cancer, normal and apoptotic C6 cells on the basis of changes in intracellular viscosity†
Abstract
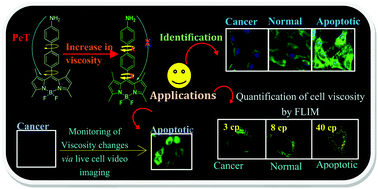
The applications of a bodipy based probe 1 for the identification of diseased cell population out of normal cells on the basis of changes in intracellular viscosity have been explored. Probe 1 works on the principle of restriction of rotation in viscous medium and the molecular rotor nature of probe 1 is supported by low temperature 1H NMR and variable dihedral angle DFT and TD-DFT studies. More importantly, probe 1 is the first probe which shows its practical application in monitoring micro-viscosity changes in a cell based model system of undifferentiated, differentiated and apoptotic C6 glial cells. Further, probe 1 can effectively monitor the apoptosis pathway by showing an increase in fluorescence intensity from cancerous cells to apoptotic cells via real time live-cell video imaging. Moreover, the viscosity changes in living cells were proved by fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIM) studies, flow cytometry using Annexin-V and Bcl-xl expression by immunocytofluorescence (ICC) and western blot analysis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...