Citrate-capped iron oxide nanoparticles impair the osteogenic differentiation potential of rat mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
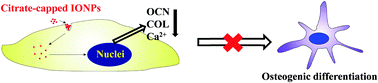
Surface modification of iron oxide nanoparticles may cause unexpected impact upon interaction with cells, such as cytotoxicity and change in the differentiation potential of stem cells. In this study, two kinds of iron oxide nanoparticles with different surface chemistries, i.e. one in its pristine form (P-NPs) without extra capping molecules and the other coated with citrate (C-NPs), and with similar sizes, ∼10 nm, as measured by transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffractometry, were prepared. Both P-NPs and C-NPs aggregated to some extent in water, with hydrodynamic diameters of 211.4 ± 29 and 128.6 ± 6.3 nm, and surface zeta potential values of +23.5 ± 0.3 and −49.6 ± 0.5 mV, respectively. However, both NPs further aggregated to a similar extent with hydrodynamic diameters of 260 ± 5.5 and 214 ± 6.4 nm and with a slightly negative surface charge (∼−10 mV) in cell differentiation media. After being incubated with rat mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for 14 d, both types of NPs showed similar cell uptake kinetics and final intracellular iron content, i.e. 53.3 pg per cell for P-NPs and 59.9 pg per cell for C-NPs, and minimal cytotoxicity at a concentration below 100 μg mL−1. The adipogenic differentiation potential of MSCs was unaltered regardless of the NP types, and the P-NPs did not have an obvious impact on the osteogenic differentiation potential of MSCs. The osteogenic differentiation potential of the MSCs, however, was significantly impaired by incubation with the C-NPs, as evidenced by significantly reduced expression of osteogenic markers, namely collagen type I (COL) and osteocalcin (OCN) and calcium deposition. The uptake of C-NPs and surface-anchored citrate molecules were found to have a synergistic effect.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...