Germanium encapsulated in sulfur and nitrogen co-doped 3D porous carbon as an ultra-long-cycle life anode for lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
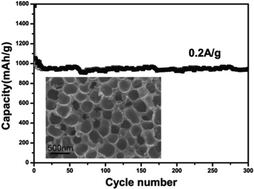
Germanium (Ge) has been considered as a promising anode material for Li-ion batteries because of its theoretical capacity (1600 mA h g−1). However, its poor electrochemical performances resulting from the large volume variation during Li–Ge alloy/dealloy processes prevent its practical application. Herein, we designed a 3D core/shell structure by encapsulation of Ge in a sulfur (S) and nitrogen (N) co-doped three-dimensionally (3D) interconnected macroporous carbon matrix (denoted as Ge@S,N-3DPC). The 3D porous structure can not only buffer the volume change during alloy/dealloy processes, but also facilitate the electrolyte to soak in, offering fast ion/electron pathways. What's more, the co-doping of S and N in carbon could introduce more defects and active sites, which can also help to improve the interfacial adsorption and electrochemical behaviors. When used as an anode material for LIBs, the Ge@S,N-3DPC shows excellent electrochemical performances (1000 mA h g−1 at 200 mA g−1), outstanding cycling stability (94% capacity retention after 300 cycles) and high rate capability (358 mA h g−1 at 10 A g−1). This work develops a general strategy to improve the electrochemical performance of these alloy-type electrode materials with huge volume change in the energy storage area.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...