Gamma titanium phosphate as an electrode material for Li-ion and Na-ion storage: performance and mechanism†
Abstract
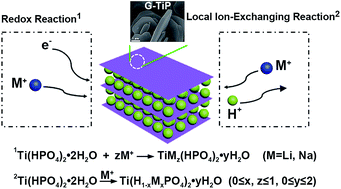
Gamma titanium phosphate (G-TiP) possesses a lamellar framework with larger interlayer spacing than α-type TiP, in which the protons within the P–OH groups can be exchanged by alien ions. Herein, the electrochemical performance of the bulk G-TiP in both lithium and sodium storage has been systematically investigated. The results reveal that the layered G-TiP can store both Li+ and Na+ ions via a local ion exchange process and redox reaction in a wide voltage range. Despite the large radius of Na+, G-TiP exhibits a higher structural tolerance upon (de)sodiation and better capacity retention when cycled at low voltage. For a Na-ion cell, the G-TiP electrode delivers a specific capacity of 161.3 mA h g−1 within 0.1–2.8 V, showing an obvious plateau in the range of 1.6–2.2 V with a solid solution reaction. For a Li-ion cell, a reversible capacity of 109 mA h g−1 is attained within 0.8–2.8 V, and a voltage plateau occurs at 2.2–2.6 V.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...