Mediator-free Z-scheme photocatalytic system based on ultrathin CdS nanosheets for efficient hydrogen evolution†
Abstract
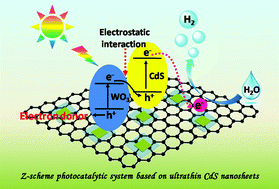
The development of a facile and scalable method to synthesize ultrathin CdS nanosheets and fabricate a mediator-free Z-scheme photocatalytic (PC) system based on ultrathin CdS nanosheets are highly challenging. Herein, we present a one-pot diethylenetriamine-assisted method for synthesizing ultrathin CdS nanosheets (CdS NSs) and their composites with reduced graphene oxide (CdS-NSs/RGO), and then we rationally design a mediator-free Z-scheme PC system composed of electrostatically interacting CdS NSs or CdS-NSs/RGO and WO3 nanosheets (WO3 NSs) for efficient PC H2 evolution. The results of PC tests show that in the presence of an optimized amount of RGO, the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution activity of CdS-NSs/RGO is higher than that of pure ultrathin CdS NSs. Furthermore, when combined with WO3 NSs to fabricate Z-scheme PC systems, the composite photocatalysts exhibit higher photocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution in water–ethanol mixtures compared with their pure components. Special ultrathin and 2D sheet-like structure, electrostatic interaction, suitable energy band structure and assistance of RGO as a supporting matrix and an electron collector contribute to the effortless transfer of electrons, resulting in enhanced PC performance. Impressively, the as-fabricated mediator-free Z-scheme PC system can also be used as a photocathode for photoelectrochemical (PEC) H2 evolution. Our present work may provide a promising strategy to fabricate efficient PC and PEC systems for solar-to-fuel energy conversion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...