A novel hollow sphere bismuth oxide doped mesoporous carbon nanocomposite material derived from sustainable biomass for picomolar electrochemical detection of lead and cadmium†
Abstract
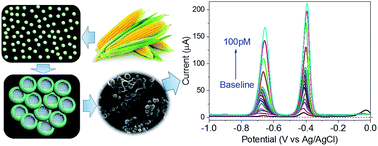
A novel ultrasensitive, selective and low cost electrochemical sensor based on a hollow sphere bismuth oxide doped mesoporous carbon aerogel nanocomposite derived from a sustainable biomass material was successfully fabricated for simultaneous Pb2+ and Cd2+ detection at picomolar levels. In this nanocomposite material, we successfully brought together the advantages of an extraordinarily large surface area biomass derived carbon matrix with mesopores for analyte pre-enrichment and the excellent electroanalytical activity of the bismuth oxide hollow sphere structure for highly sensitive heavy metal sensing. Under optimized conditions, this electrode material exhibited a very low detection limit of 1.72 pM for Pb2+ and 1.58 pM for Cd2+ under ambient conditions, the lowest ever limit of detection recorded for the detection of both Pb2+ and Cd2+ using activated carbon. Furthermore, two wide linear ranges from 0.5 pM to 10 pM and from 10 pM to100 pM were observed due to the differences of adsorption dynamics at different metal ion concentration ranges. The nanocomposite sensor material demonstrated excellent reproducibility and great resistance to interference. Furthermore, the application for real water analysis was demonstrated and the result was highly consistent with the measurement from inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...