Sulfur to oxygen substitution in BiOCuSe and its effect on the thermoelectric properties
Abstract
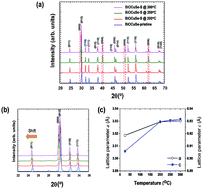
The effects of S doping at the oxygen site on the thermoelectric properties of BiOCuSe have been investigated. The partial substitution of S ions at the O sites of BiOCuSe was achieved by sulfurization using CS2 gas. Analysis of the powder X-ray diffraction data indicates that the ZrCuSiAs structure of BiOCuSe is retained after sulfurization. Substitution of O with S leads to an increase in the lattice parameters and a decrease in the band gap. The electrical conductivity rises due to the increase of the electronic contribution with doping. S-doped BiOCuSe materials behave as a p-type semiconductor. The thermoelectric properties of S-doped BiOCuSe materials can be understood through the analysis of the electronic band structure and the density of states close to the Fermi level. The substitution of O sites with S provides possible directions toward the enhancement of the thermoelectric figure of merit of oxide materials with low electrical conductivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...