Highly efficient TiO2 single-crystal photocatalyst with spatially separated Ag and F− bi-cocatalysts: orientation transfer of photogenerated charges and their rapid interfacial reaction†
Abstract
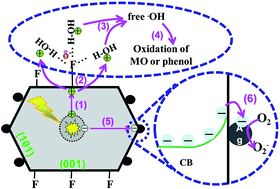
For an efficient photocatalytic system, the rapid orientation transfer of photogenerated electron–hole pairs inside the photocatalyst and their effective interfacial catalytic reactions are significantly critical for achieving a high photocatalytic performance. However, it is quite difficult for a general photocatalyst to realize the crucial functions. In this study, the above idea was easily realized via a coupling strategy of crystal-facet engineering and spatially separated cocatalyst modification, namely, a TiO2 single-crystal photocatalyst with spatially separated Ag and F− bi-cocatalysts (Ag/F–TiO2). In this case, the F ions (as a hole cocatalyst) and Ag nanoparticles (as an electron cocatalyst) were selectively modified on the hole-rich (001) and electron-rich (101) facets of TiO2 single crystals, respectively. Photocatalytic results demonstrated that the resultant spatially separated Ag/F–TiO2 photocatalyst exhibited an obviously higher photocatalytic performance than pure TiO2, single-cocatalyst modified TiO2 (F–TiO2 and Ag/TiO2) and randomly Ag-deposited TiO2 (Ag/F–TiO2(R)). The main reason for the enhanced photocatalytic activity can be attributed to the excellent synergistic effect of orientation transfer of photogenerated charges and their rapid interfacial reaction via the efficient coupling strategy of crystal-facet engineering and cocatalyst modification, namely, the TiO2 single crystal structure can self-induce the orientation transfer of photogenerated charges to different crystal facets, while the spatially separated cocatalysts function as the effective active sites for the rapid interfacial catalytic reactions of those spatially separated charges (Ag nanoparticles on the (101) facets work as the active centres for oxygen-reduction reactions, and F ions on the (001) facets serve as the active sites for oxidation reactions of organic substances). The present coupling strategy of crystal-facet engineering and cocatalyst modification may also provide new ideas for the design and preparation of other highly efficient semiconductor photocatalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...