Cobalt phosphate nanoparticles decorated with nitrogen-doped carbon layers as highly active and stable electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction†
Abstract
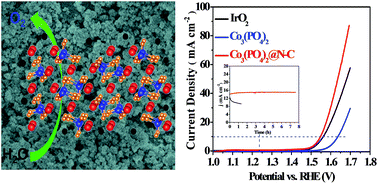
One promising approach to the production of clean hydrogen energy from electrochemical water splitting mainly relies on the successful development of earth-abundant, highly efficient and stable electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER). Herein, we report the synthesis of robust cobalt phosphate nanoparticles (NPs) decorated with nitrogen-doped carbon layers (denoted as Co3(PO4)2@N-C) using O-phospho-DL-serine as both phosphate and carbon sources by hydrothermal treatment. The obtained Co3(PO4)2@N-C catalyst exhibits a remarkable electrocatalytic performance for the OER in alkaline media. A current density of 10 mA cm−2 is generated at a overpotential of only 317 mV with a small Tafel slope of 62 mV per decade in 1 M KOH electrolyte, which is even superior to those of state-of-the-art noble metal catalysts such as benchmark IrO2 catalysts. Notably, the Co3(PO4)2@N-C electrode shows excellent stability evaluated by 1000 potential cycles and operation with a high current density at a fixed potential for 8 h, which is highly desirable for a promising electrocatalyst. The excellent activity can be attributed to the unique network structure of materials, a large number of active sites and good conductivity under catalytic conditions. Our findings imply the possibility for the development of robust and cost-efficient cobalt phosphate as a promising candidate to replace high-cost and scarce noble metal catalysts for electrochemical water splitting.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...