Impregnation of metal ions into porphyrin-based imine gels to modulate guest uptake and to assemble a catalytic microfluidic reactor†
Abstract
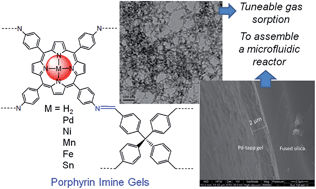
A series of (metallo)porphyrin imine gels have been synthesized based on imine chemistry. The resulting aerogels have sponge-like porous networked structures consisting of interconnected nanoparticles with hierarchical porosity. The aerogels have high specific surface areas (up to 719 m2 g−1) and large pore volumes (up to 2.60 cm3 g−1). The effect of metal ions on the uptake of gases in these aerogels was investigated. The impregnation of various metal ions (Pd(II), Ni(II), Mn(III), Fe(III) and Sn(IV)) enhances the uptake capacity of various gases (e.g., CO2) despite their higher densities. Among the metal ions, Pd(II) is the best to increase the adsorption capacity and the isosteric heat of CO2 adsorption. The Pd-tapp–A4 aerogel exhibits CO2 volumetric uptake (1.62 mmol g−1, 7.13 wt% at 298 K, 1 bar) with a high isosteric heat of adsorption (40.0 kJ mol−1). The gels also show potential applications in catalysis because of their unique hierarchical porosity and the availability of metal centers. In combination with microfluidic technology, a catalytic gel capillary reactor has been assembled with the Pd-tapp–A4 gel supported on the inner surface of a functionalized capillary.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...