Vertically stacked bilayer CuCo2O4/MnCo2O4 heterostructures on functionalized graphite paper for high-performance electrochemical capacitors†
Abstract
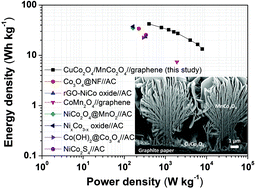
Cobaltite systems with spinel structures are promising cathode materials for next-generation high-performance electrochemical capacitors because of their high electrochemical stability. However, increasing the mass loading of active materials without sacrificing the geometry of the nanostructures remains a challenge. In this study, we propose vertically stacked bilayer spinel heterostructures constructed from hierarchical CuCo2O4/MnCo2O4 on graphite paper as highly capable supercapacitor electrodes. A two-step hydrothermal method with post annealing treatment is used in the preparation of the heterostructures. The CuCo2O4/MnCo2O4 electrode delivers a remarkable specific capacitance of 1434 F g−1 at 0.5 A g−1, considerable high-rate capability (810 F g−1 at 15 A g−1), and an excellent cycling stability, maintaining 81.4% at 10 A g−1 after 5000 cycles. An electrochemical capacitor device operating at 1.6 V is also constructed using CuCo2O4/MnCo2O4 and graphene as positive and negative electrodes, respectively. The device shows a high energy density of 42.1 W h kg−1 at a power density of 400 W kg−1, as well as good cycling stability (88.4% retention after 10 000 cycles). The concept of stacking heteronanostructures can potentially enrich the electrochemical performance of metal oxides for next-generation electrochemical capacitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...