An electrochemically functional layer of hydrogenase extract on an electrode of large and tunable specific surface area†
Abstract
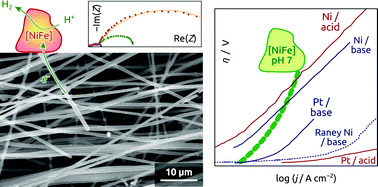
Electrode supports are generated by electrospinning of polyacrylonitrile fibers and subsequent coating of a thin electrically conductive TiO2 layer by atomic layer deposition. The supports are then functionalized with a [NiFe]-hydrogenase-containing membrane fraction from Escherichia coli and are characterized structurally and electrochemically. The hydrogenase suspension generates a micron-thick organic film around the fiber mat, which exhibits electrocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution. Furthermore, the electrode geometric surface area is varied systematically via the electrospinning procedure, which reduces the charge transfer resistance and increases the hydrogen evolution current density to >500 μA cm−2 at 0.3 V overpotential.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...