New Co(OH)2/CdS nanowires for efficient visible light photocatalytic hydrogen production†
Abstract
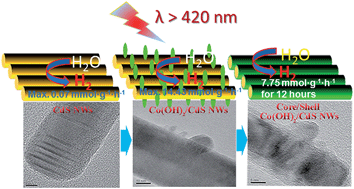
Through a facile impregnation synthesis, new noble-metal-free Co(OH)2/CdS nanowires (NWs) have been developed for photocatalytic hydrogen production. The loading of Co(OH)2 on CdS NWs can effectively accelerate the charge separation and transfer in photocatalytic reactions, leading to an enhanced H2 production rate (HPR). The optimum HPR based on Co(OH)2/CdS reaches 14.43 mmol h−1 g−1 under visible light (λ ≥ 420 nm) irradiation, which is 206 times higher than for the pristine CdS NWs and even 3 times higher than for 1 wt% Pt/CdS NWs as a benchmark. Impressively, core–shell structural Co(OH)2/CdS NWs formed by visible-light-induced self-assembly during the photocatalytic reaction. And the core–shell structural characteristics of the Co(OH)2/CdS NWs can effectively avoid light corrosion, leading to a stable HPR in 12 hours duration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...