Novel AgPd hollow spheres anchored on graphene as an efficient catalyst for dehydrogenation of formic acid at room temperature†
Abstract
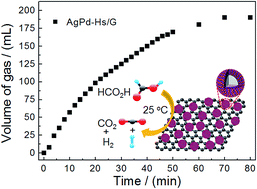
Highly dispersed AgPd hollow spheres anchored on graphene (denoted as AgPd-Hs/G) were successfully synthesized through a facile one-pot hydrothermal route for the first time. The fabrication strategy was efficient and green by using L-ascorbic acid (L-AA) as the reductant and trisodium citrate dihydrate as the stabilizer, without employing any seed, surfactant, organic solvent, template, stabilizing agent, or complicated apparatus. The as-synthesized AgPd-Hs/G catalyst exhibits a sphere-shaped hollow structure with an average diameter of about 18 nm and a thin wall of about 5 nm. The hollow architecture with a thin wall and excellent dispersion on the graphene ensure that most of the atoms are located on the surface or sub-surface, which provides reactive catalytic sites for the dehydrogenation of formic acid. Therefore, a superior catalytic effect was achieved compared with other catalysts such as Pd/G and AgPd/C. The as-synthesized AgPd-Hs/G exhibits a catalytic activity with an initial turnover frequency (TOF) value as high as 333 mol H2 mol−1 catalyst h−1 even at room temperature (25 °C) toward the decomposition of formic acid. The present AgPd-Hs/G with efficient catalysis on the dehydrogenation of formic acid without any CO generation at room temperature can pave the way for a practical liquid hydrogen storage system and therefore promote the application of formic acid in fuel cell systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...