Photo-activity and low resistivity in N/Nb Co-doped TiO2 thin films by combinatorial AACVD†
Abstract
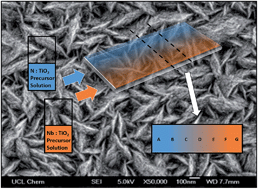
A combinatorial aerosol assisted chemical vapour deposition (cAACVD) cation–anion co-doping study has been undertaken for the first time, which investigates the interplay of nitrogen and niobium co-dopants and the resultant functional properties within TiO2 thin films. This study advantageously creates a single doped TiO2 thin film which incorporates many compositions that transition from nitrogen doped TiO2 to niobium doped TiO2 across the film's width, in a single deposition. The film was split into a grid and the physical properties of each grid position characterised by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and UV-visible transmission spectroscopy (UV/Vis). Functional properties such as photo-catalytic activity, water contact angles and resistivity were also characterised. The study was successful in creating and identifying the optimum dopant concentration at which these TiO2 films exhibited both a high rate of photo-activity and favourable transparent conducting oxide (TCO) properties. Whilst most co-doping studies report relatively homogenous film, the inhomogeneity of these films allows both functional properties to exist in conjunction. To the authors knowledge this is the first instance cation and anion co-doping has been explored in the combinatorial regime.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...