Synthesis, structure and electrical properties of N-doped Li3VO4
Abstract
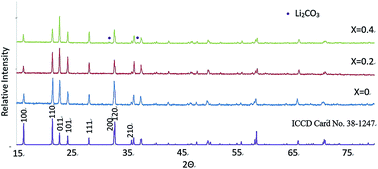
N-doped Li3VO4 of general formula Li3+xVO4−xNx was prepared by solid state reaction of Li3N, V2O5 and either Li2CO3 or LiOH·H2O. A solid solution based on the low temperature β polymorph of Li3VO4 was obtained with composition 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.2. Structural studies by X-ray and neutron powder diffraction confirmed the partial replacement of oxygen on the O(1) sites by N together with creation of an equal number of Li+ ions which are located off-centre in adjacent octahedral Li(3) sites. Electrical property measurements on sintered pellets using impedance spectroscopy showed that the solid solutions are modest conductors of Li+ ions, consistent with the partial occupancy of Li+ ions in the interstitial octahedral sites. The activation energy for conduction of samples prepared using LiOH·H2O, ∼1.91 eV, is much greater than for samples prepared at higher temperature, using Li2CO3, ∼0.78 eV; it is speculated that this is due to ion trapping in Lii˙/N0′ defect clusters. This study represents a relatively new method for doping Li+ ions into a structure by aliovalent anion doping: partial replacement of O by N is compensated by creation of interstitial Li+ ions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...