Time-structuring in the evolution of 2D nanopatterns through interactions with substrate
Abstract
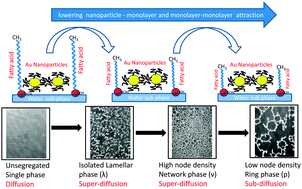
Hydrophobic dodecanethiol capped gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are found to self-assemble into two-dimensional patterns in monolayers of amphiphiles spread at the air–water interface of a Langmuir trough. In this communication we investigate the role of the nanoparticle–monolayer (FNMA) and monolayer–monolayer (FMMA) lipophilic attraction in influencing morphology and dynamics of AuNP cluster patterns in fatty acid monolayers. FNMA and FMMA are progressively varied by changing n, where n is the number of –CH2 groups in the alkyl tails of the amphiphilic fatty acid (CH3(CH2)nCOOH) molecules forming the monolayer. Compressibility measurements on the pristine and nanoparticle–laden monolayers show that, while the compressibility of the pristine monolayer decreases with increasing n, pointing to a progressive increase in FMMA, the effect of nanoparticles (increase in compressibility or lowering of FMMA) is discernible only for 14 < n < 22. The corresponding pattern morphology, observed with a Brewster Angle Microscope (BAM) at an in-plane resolution of 450 nm for 6 hours, reveals that there are essentially three stages in pattern evolution, lamellae of Au nanoclusters spread over the fatty-acid monolayer background (the λ state) followed by a network of nanoclusters with high node density (the ν state) and finally rings (circular/elongated) of random sizes with very low node density (the ρ state), evolving from an initial unsegregated state, without appreciable change in the average nanoparticle number density over the field of view. Increasing FNMA alongwith FMMA is found to shift a certain state to later times, thus playing the role of a viscous drag and introducing a delay in the timeline. The mean square fluctuation of BAM intensity remains flat and then decays as f(ξ) = ξ2H over smaller length scales, where ξ is the spatial separation and H the Hurst exponent. The study of f(ξ) over time reveals the growth of a sub-diffusive regime (H < 0.5) at the intermediate length scale, in almost all the films coinciding with the emergence of the ρ state. The growth of this sub-diffusive regime is slower for stronger FNMA and FMMA, the interactions thus acting as control parameters in dictating the time structure of the spatio-temporal patterns.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...