Microdynamics mechanism of D2O absorption of the poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)-based contact lens hydrogel studied by two-dimensional correlation ATR-FTIR spectroscopy
Abstract
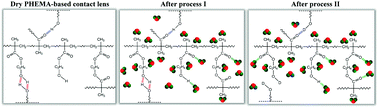
A good understanding of the microdynamics of the water absorption of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PHEMA)-based contact lens is significant for scientific investigation and commercial applications. In this study, time-dependent ATR-FTIR spectroscopy combined with the perturbation correlation moving-window two-dimensional (PCMW2D) technique and 2D correlation analysis was used to study the microdynamics mechanism. PCMW2D revealed that D2O took 3.4 min to penetrate into the contact lens. PCMW2D also found the PHEMA-based contact lens underwent two processes (I and II) during D2O absorption, and the time regions of processes I and II are 3.4–12.4 min and 12.4–57.0 min. According to 2D correlation analysis, it was proved that process I has 5 steps, and process II has 3 steps. For process I, the first step is D2O hydrogen-bonding with “free” C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O in the side chains. The second step is the hydrogen bond generation of the O–H⋯O–D structure between D2O and “free” O–H groups in the side chain ends. The third step is the hydrogen bond generation of D2O and the “free” C
O in the side chains. The second step is the hydrogen bond generation of the O–H⋯O–D structure between D2O and “free” O–H groups in the side chain ends. The third step is the hydrogen bond generation of D2O and the “free” C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O groups close to the crosslinking points in the contact lens. The fourth and the fifth steps are the hydration of –CH3 and –CH2– groups by D2O, respectively. For process II, the first step is the same as that of process I. The second step is the hydrogen bonds breaking of bonded O–H groups and the deuterium exchange between D2O and O–H groups in the side chain ends. The third step is also related to the deuterium exchange, which is the hydrogen bonds regeneration between the dissociated C
O groups close to the crosslinking points in the contact lens. The fourth and the fifth steps are the hydration of –CH3 and –CH2– groups by D2O, respectively. For process II, the first step is the same as that of process I. The second step is the hydrogen bonds breaking of bonded O–H groups and the deuterium exchange between D2O and O–H groups in the side chain ends. The third step is also related to the deuterium exchange, which is the hydrogen bonds regeneration between the dissociated C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O groups and the new O–D.
O groups and the new O–D.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...