Cytoskeletal motor-driven active self-assembly in in vitro systems
Abstract
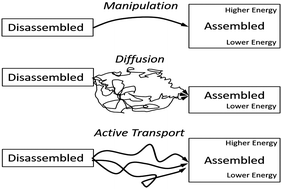
Molecular motor-driven self-assembly has been an active area of soft matter research for the past decade. Because molecular motors transform chemical energy into mechanical work, systems which employ molecular motors to drive self-assembly processes are able to overcome kinetic and thermodynamic limits on assembly time, size, complexity, and structure. Here, we review the progress in elucidating and demonstrating the rules and capabilities of motor-driven active self-assembly. We focus on the types of structures created and the degree of control realized over these structures, and discuss the next steps necessary to achieve the full potential of this assembly mode which complements robotic manipulation and passive self-assembly.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...