Radical transfer in E. coli ribonucleotide reductase: a NH2Y731/R411A-α mutant unmasks a new conformation of the pathway residue 731†
Abstract
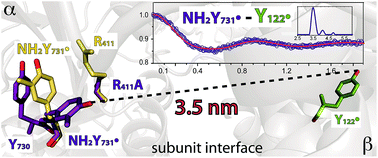
Ribonucleotide reductases (RNRs) catalyze the conversion of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides in all living organisms. The catalytic cycle of E. coli RNR involves a long-range proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) from a tyrosyl radical (Y122˙) in subunit β2 to a cysteine (C439) in the active site of subunit α2, which subsequently initiates nucleotide reduction. This oxidation occurs over 35 Å and involves a specific pathway of redox active amino acids (Y122 ↔ [W48?] ↔ Y356 in β2 to Y731 ↔ Y730 ↔ C439 in α2). The mechanisms of the PCET steps at the interface of the α2β2 complex remain puzzling due to a lack of structural information for this region. Recently, DFT calculations on the 3-aminotyrosyl radical (NH2Y731˙)-α2 trapped by incubation of NH2Y731-α2/β2/CDP(substrate)/ATP(allosteric effector) suggested that R411-α2, a residue close to the α2β2 interface, interacts with NH2Y731˙ and accounts in part for its perturbed EPR parameters. To examine its role, we further modified NH2Y731-α2 with a R411A substitution. NH2Y731˙/R411A generated upon incubation of NH2Y731/R411A-α2/β2/CDP/ATP was investigated using multi-frequency (34, 94 and 263 GHz) EPR, 34 GHz pulsed electron–electron double resonance (PELDOR) and electron–nuclear double resonance (ENDOR) spectroscopies. The data indicate a large conformational change in NH2Y731˙/R411A relative to the NH2Y731˙ single mutant. Particularly, the inter-spin distance from NH2Y731˙/R411A in one αβ pair to Y122˙ in a second αβ pair decreases by 3 Å in the presence of the R411A mutation. This is the first experimental evidence for the flexibility of pathway residue Y731-α2 in an α2β2 complex and suggests a role for R411 in the stacked Y731/Y730 conformation involved in collinear PCET. Furthermore, NH2Y731˙/R411A serves as a probe of the PCET process across the subunit interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...