Trimetallaborides as starting points for the syntheses of large metal-rich molecular borides and clusters†
Abstract
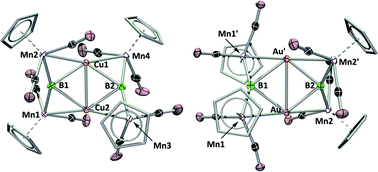
Treatment of an anionic dimanganaborylene complex ([{Cp(CO)2Mn}2B]−) with coinage metal cations stabilized by a very weakly coordinating Lewis base (SMe2) led to the coordination of the incoming metal and subsequent displacement of dimethylsulfide in the formation of hexametalladiborides featuring planar four-membered M2B2 cores (M = Cu, Au) comparable to transition metal clusters constructed around four-membered rings composed solely of coinage metals. The analogies between compounds consisting of B2M2 units and M4 (M = Cu, Au) units speak to the often overlooked metalloid nature of boron. Treatment of one of these compounds (M = Cu) with a Lewis-basic metal fragment (Pt(PCy3)2) led to the formation of a tetrametallaboride featuring two manganese, one copper and one platinum atom, all bound to boron in a geometry not yet seen for this kind of compound. Computational examination suggests that this geometry is the result of d10–d10 dispersion interactions between the copper and platinum fragments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...