The electrochemical 4-chlorophenol sensing properties of a plasma-treated multilayer graphene modified photolithography patterned platinum electrode†
Abstract
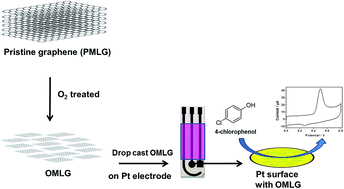
The present work describes the electrochemical 4-chlorophenol (4-CP) sensing properties of multilayer graphene samples (MLG). In order to enhance the presence of oxygen functional groups and to increase the edge plane defects, oxygen plasma treatment is adopted. Raman, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) characterizations are used to investigate the effect of plasma treatment on MLG. Compared to pristine MLG, the oxygen plasma treated one shows increased oxidation current towards 4-CP. The sensor data exhibit high sensitivity and stability with high anti-interference property in the presence of other phenolic compounds including phenol, bisphenol, 2,3-chlorophenol, 2,3,4-nitrophenol and inorganic ions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...