Gel electrophoretic analysis of differently shaped interacting and non-interacting bioconjugated nanoparticles†
Abstract
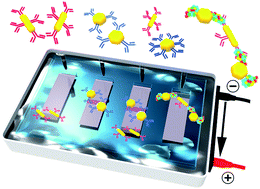
The use of a simple gel electrophoretic method to study mixtures of differently shaped biofunctionalized nanoparticles (NP's) that undergo bioaffinity interactions is demonstrated. Both gold nanorods (NR's) and quasi-spherical nanoparticles (qNS's) were functionalized with an interacting antigen and antibody pairing (alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) protein and antiAAT) or non-interacting antibody controls (antiBNP). Gel-based measurements were accompanied with transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and UV-vis spectroscopy analysis before and after separation. Initial measurements of NR and qNS bioconjugates suspended individually were applied to optimize the gel separation conditions and it was demonstrated that higher particle uniformities could be obtained relative to the initial stock solutions. A series of NR and qNS mixtures prepared at various stoichiometric ratios were then compared for both interacting (antiAAT–AAT) and non-interacting (antiAAT–antiBNP) particle conjugates. Both gel images and extinction measurements were utilized to demonstrate reduced NP concentrations transported along the gel due to bioaffinity-induced NP assembly. This confirmed that gel electrophoresis can be extended to identifying particle aggregation associated with protein bioaffinity interactions as well as being an established tool for separating particles based on size, shape and surface chemistry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...