Nonprecious mixed oxide catalysts Co3AlO and Co2NiAlO derived from nanoflowerlike cobalt-based hydrotalcites for highly efficient oxidation of nitric oxide†
Abstract
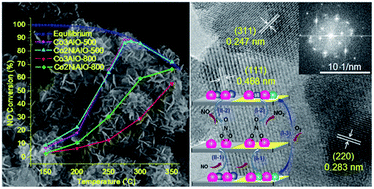
Nonprecious mixed oxide catalysts Co3AlO-T and Co2NiAlO-T (T = 500, 800) were obtained from thermal decomposition of nanoflowerlike Co3Al-HT and Co2NiAl-HT hydrotalcite-like precursors at 500 and 800 °C, which were synthesized by a facile co-precipitation method, and systematically characterized by combinational techniques. The mixed oxide catalysts mainly consisted of homogeneous and stable non-stoichiometric cobalt-based spinel phases Co(Co,Al)2O4 and Ni(Co,Al)2O4. The 500 °C calcined catalysts showed nanoflowerlike morphology, while the 800 °C calcined catalysts presented disorderly stacked states consisting of severely agglomerated irregular nanoparticles. The catalysts Co3AlO-500 and Co2NiAlO-500 presented excellent catalytic NO oxidation performance, with the maximum conversion efficiency ca. 88.8% and 87.6% (285 °C), respectively, which is much higher than those of Co3AlO-800 and Co2NiAlO-800 (55.6% and 66.6% at 350 °C). The excellent catalytic NO oxidation performance of Co3AlO-500 and Co2NiAlO-500 could be attributed to the much larger amount of surface active sites endowed by these catalysts with smaller crystallite sizes of cobalt-based spinel phases, higher specific surface areas, and mesoporous structure. The active sites and NO oxidation pathways of the present catalysts were tentatively proposed. Although Co2NiAlO-500 possessed a slightly smaller amount of active sites (Co3+ and Ni3+ associated with surface adsorbed oxygen), compared to Co3AlO-500 with active sites (Co3+ associated with surface adsorbed oxygen), catalyst Co2NiAlO-500 possessed higher reducibility, leading to their similar desorption amount of NO2, thus similar NO oxidation performance. Moreover, the lower cost of catalyst Co2NiAlO-500 gives it a greater potential for practical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...