Influence of siloxane on the transport of ZnO nanoparticles from different release pathways in saturated sand†
Abstract
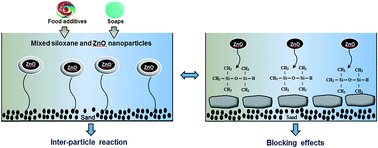
The production of nanomaterials (NMs) is expected to grow continuously, yet their transformation, transport, release mechanisms, and interactions with contaminants under environmental conditions remain poorly understood. Few studies have investigated the effects of contaminants on fate and transport of NMs, especially siloxanes that are widely found in products. It is hypothesized that the model contaminant, siloxane (e.g., 1,1,3,3-tetramethyldisiloxane (TMDS)) may influence the mechanisms and transport kinetics of NMs under different release pathways. Sand column experiments were carried out under two different scenarios: the release from a mixed TMDS and nano-ZnO suspension (A) and the release of nano-ZnO from sand contaminated with TMDS (B). Results show that interparticle reactions are dominant in (A) and particle–porous interactions are responsible for blocking effects governing in (B). Insights, especially the kinetics of nano-ZnO from co-transport by a contaminant and from porous media preloaded with a contaminant, and environmental factors affecting the release and retention of nano-ZnO in saturated sand are unveiled. These two dominant transport mechanisms (e.g., interparticle reactions and blocking effects) were derived. This study indicates that the release of ZnO NPs is influenced by the presence of TMDS; the extent of mobility and their transport pathways depend on the pre-existence of TMDS in porous media.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...