A RAFT copolymerization of NIPAM and HPMA and evaluation of thermo-responsive properties of poly(NIPAM-co-HPMA)†
Abstract
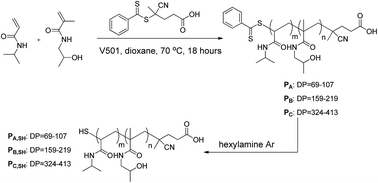
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) has attracted intensive interest for bio-medical applications due to its unique thermal properties whereby it displays a lower critical solution temperature (LCST) close to body temperature. It is well known that the LCST of PNIPAM can be tuned by incorporating a second component. In this study, a library of (co)polymers of NIPAM and N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide (HPMA) with varying molecular weight (MW), composition, and end functionality were synthesized by Reversible Addition-Fragmentation chain Transfer (RAFT) polymerization to systematically investigate how these factors influence their thermo-responsive behavior. Our findings include: (1) the LCST of NIPAM-co-HPMA (co)polymers increases with HPMA content (FHPMA) in the temperature range from 29 to 92 °C; (2) the LCST of the polymers is significantly higher when the hydrophobic dithiobenzoate end-group is converted to a thiol-group, however, this influence becomes less pronounced for high MW polymers; (3) the MW of the copolymers has a negligible influence on the LCST. This systematic study investigating the effects of such influencing factors as MW, end group, and polymer composition on the LCST of NIPAM-containing polymers provides new insights into this class of thermo-responsive polymers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...