Quantitative measurements of charge carrier hopping transport properties in depleted-heterojunction PbS colloidal quantum dot solar cells from temperature dependent current–voltage characteristics
Abstract
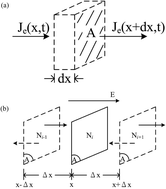
Non-conventional (anomalous) current–voltage characteristics are reported with increasing frequency for colloidal quantum dot-based (CQD) solar cells. The causes of S-shaped or negative-exponential J–V curves are not well understood. Many attempts made to explain these behaviors do not fully consider the physical electronic transport processes inside the solar cell within a hopping exciton and/or dissociated charge carrier framework. In this paper physical optoelectronic processes in heterojunction PbS CQD solar cells exhibiting anomalous J–V characteristic curves which are likely to share common origins with other QD solar cells with similar J–V characteristics are studied at 300 K, 250 K, 200 K, 150 K and 100 K and a suitable theoretical model of purely hopping transport is developed. Hopping exciton-dissociation-generated hole accumulation at, and near, the CQD/metal interface leading to a space-charge layer (SCL) of temperature-dependent width is predicted, and a new “hopping” Einstein relation is derived and experimentally demonstrated. A two-diode-equivalent charge carrier transport model is invoked and quantitative measurements of hopping carrier transport parameters are made both in the forward region and the reverse SCL, based on the J–V characteristics at those temperatures. The quantitative results add physical insight to the transport mechanism in glass/FTO/TiO2/PbS QD/MoO3/Au/Ag solar cells, in the bulk CQD film as well as within the SCL. These insights can be used for potential design improvement to maximize solar power conversion efficiencies, such as optimal dot-to-dot distance for maximizing charge carrier diffusivity and mobility.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...