Xyloglucan as a mitomycin C carrier to reverse multidrug resistance
Abstract
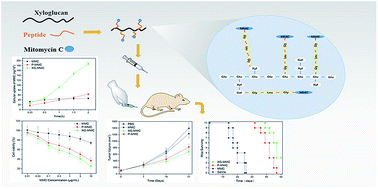
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is still considered as the third highest cause of cancer death in developing countries. In our previous study, we confirmed that the galactose residues of natural polysaccharide xyloglucan (XG) turns out to be selected uptake by asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR) and the xyloglucan can be used as drug carriers and achieve some enhancement in the therapeutic effect of HCC via ASGPR mediated endocytosis. In this study, we selected mitomycin C (MMC) as the anticancer model drug and a macromolecular drug delivery system (DDS) with different degrees of substitution that was synthesized by conjugating mitomycin C with xyloglucan. The degree of substitution of xyloglucan–mitomycin C conjugates (XG–MMC) was about 9.7%. Another sample obtained a higher degree of substitution (p-MMC) of approximately 31%. The content of MMC in XG–MMC and p-MMC was determined and calculated to be about 3.1% and 6.4%, respectively. In the in vitro cytotoxicity experiment, the prodrugs presented higher cytotoxicity than free MMC against the drug resistant HepG2 cells. Moreover, the IC50 of XG–MMC (0.997 μg mL−1) was much lower than that of p-MMC (2.56 μg mL−1) and XG–MMC exhibited higher drug uptake amounts (187.9 ng) than that of p-MMC (63.5 ng). The in vivo cytotoxicity was also evaluated, and the result was in good agreement with the in vitro cytotoxicity experiment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...