Monodisperse AgPd alloy nanoparticles as a highly active catalyst towards the methanolysis of ammonia borane for hydrogen generation
Abstract
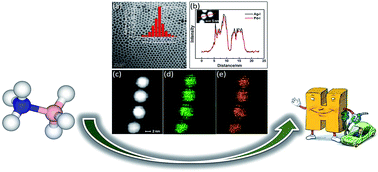
Monodisperse AgPd nanoparticles (NPs) were successfully synthesized by coreducing silver nitrate and palladium chloride in the presence of oleylamine. Characterization techniques such as transmission electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction were employed to verify the alloy nature of the obtained NPs. These AgPd NPs, supported on carbon, were found to be active catalysts for the generation of hydrogen from the methanolysis of ammonia borane at room temperature. The catalytic activity depended on the alloy composition, and the Ag30Pd70 NPs displayed the greatest activity among the tested catalysts, with a very high total turnover frequency value of 366.4 min−1 and activation energy of 37.5 kJ mol−1. In a reusability test, the Ag30Pd70/C catalyst retained 67% of its initial activity and 100% conversion after eight cycles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...