The effects of milk fat globule membrane and its individual components on dough properties and bread quality
Abstract
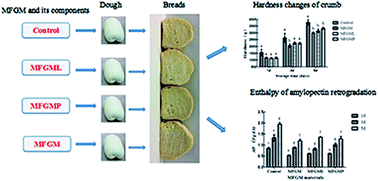
The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of the addition of milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) and its individual components such as milk fat globule membrane protein (MFGMP) and milk fat globule membrane lipid (MFGML) on dough properties, microstructure, and the staling of wheat bread. The results showed that MFGM and its individual components' incorporation modified the rheological properties of dough. The addition of the MFGM, MFGMP and MFGML in bread significantly increased the specific volume of the samples compared with the control sample. In comparison with the control sample, bread prepared with the MFGM, MFGMP and MFGML effectively avoided moisture loss. The microstructure of bread slices was observed by scanning electric microscopy and exhibited the formation of liquid films with a lamellar structure between the gluten and starch in the samples prepared with the MFGM and MFGM components. Moreover, the addition of MFGM and MFGM components implied a decrease in both the hardness and chewiness of the crumb compared to the control sample after 5 days of storage. Crumbs with the addition of MFGM and MFGMP had the typical yellowish color of a bread loaf. The presence of the MFGM and MFGM components especially for the complete MFGM could significantly decrease the enthalpy of retrogradation of amylopectin. These results clearly indicated that the addition of MFGM and its individual components could effectively improve the quality and retard staling of wheat bread.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...