Selective aliphatic/aromatic organogelation controlled by the side chain of serine amphiphiles†
Abstract
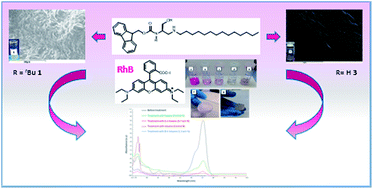
The influence of two structural features of N-Fmoc-L-serine lipoamino acids on organogel formation were investigated. These were (i) the nature of the group on the serine side chain (hydroxyl compared to O-tert-butyl) and (ii) the length of the aliphatic chain (C-14 compared to C-18). O-tert-Butylated derivatives preferentially gelled saturated hydrocarbon solvents, while compounds with the hydroxyl group in the side chain promoted the highly unusual gelation of solely aromatic solvents. Extension of the chain length of the lipoamino acid (from C-14 to C-18) decreased the selectivity observed for the shorter chain homologues. Spectroscopic analyses of these systems indicated that H-bonds, aromatic π–π stacking and van der Waals interactions are involved in the gelation processes. Rheological characterization of the gels revealed the aromatic solvent gels to be more stable than their aliphatic counterparts. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) imaging of the xerogels showed that the structure of gels formed in aromatic solvents differs significantly from those formed in aliphatic ones. The different self-assembly modes of the gelator molecules could be induced by steric effects which depend on the functional groups on the side chain. The organogels obtained were thermoresponsive, moldable and capable of self-healing. In addition, the lipoamino acids studied were phase selective gelators in biphasic mixtures of water/organic solvent and efficiently removed water soluble polluting dye rhodamine B from the aqueous phase.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...