A new method for improving the ion conductivity of anion exchange membranes by using TiO2 nanoparticles coated with ionic liquid
Abstract
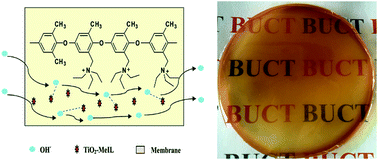
Recently a new method for increasing the ion conductivity of anion exchange membranes (AEM) was developed based on the novel materials ionic liquids (ILs). We mixed the ILs into the membrane directly instead of immobilizing onto the polymer backbone as in the traditional way. Nano-TiO2 was introduced to stabilize the ILs in the membrane. The ILs were immobilized by the nano-TiO2, acting as the “active sites” in the membrane, to enhance the mobility of the hydroxyl groups so as to increase the ion conductivity. Both pure ILs composite membranes and ILs–TiO2 composite membranes were synthesized, and their properties were compared. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy were used to analyze the structures of the composite membranes. The mechanical properties, thermal stabilities, ion conductivities, water uptakes, swelling ratios, and ion exchange capacities of the membranes were investigated. The interaction between the TiO2 and ionic liquids was confirmed by X-ray diffraction. The stability of the ILs in the membrane was measured comprehensively. All these results show that this novel method is effective and promising for AEM applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...