Thermoelectric properties of polycrystalline SnSe1±x prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering
Abstract
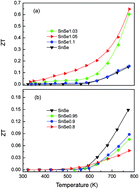
SnSe based materials have attracted much attention as high performance thermoelectric materials recently. In this work, polycrystalline SnSe1±x bulk samples were prepared by mechanical alloying (MA) combined with spark plasma sintering (SPS). When the Se stoichiometric ratio is above 1, the samples are p-type, the thermal conductivity of the samples decreased with increasing Se contents. When the Se stoichiometric ratio is under 1, the turning point from p-type to n-type was observed for all the samples, the SnSe0.8 bulk sample showed a total negative Seebeck coefficient at the measured temperature ranges from 323 to 773 K. Increases in the content of Se, lead to a considerable improvement of the power factor and a significant decrease of the thermal conductivity. Maximum ZT of ∼0.65 at 773 K was achieved for the p-type SnSe1.05 sample. n-Type SnSe0.8 polycrystals were also obtained with a peak ZT of 0.05 at 773 K.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...