Mechanistic study of visible light driven photocatalytic degradation of EDC 17α-ethinyl estradiol and azo dye Acid Black-52: phytotoxicity assessment of intermediates†
Abstract
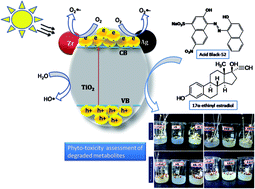
The present study evaluated the phytotoxicity of degraded intermediates of an endocrine-disrupting compound (EDC) 17α-ethinyl estradiol (EE2) and toxic azo dye Acid Black-52 (AB-52) in photocatalytic degradation. A novel bimetallic (silver and zirconium) doped TiO2 nanoparticle was synthesized for utilization in degrading these pollutants under visible light. The degradation pathway of the pollutants during photocatalytic activity was investigated by LC-MS analysis. Further, to understand the toxicity of intermediate compounds compared with the pollutants, phytotoxicity was assessed on two different seeds, Vigna radiata and Phaseolus vulgaris. Seeds treated with 100 ppm concentration of AB-52 showed low germination percentage in V. radiata (30%), and P. vulgaris (40%). Similarly, seeds treated with EE2 also showed less germination in V. radiata (40%), and P. vulgaris (50%) compared to intermediate compounds (100% germination) and revealed the less toxic nature of the degraded metabolites compared to EE2 and AB-52. Further, active radical scavenging experiments were carried out to understand the main species involved in the photocatalytic degradation process. A photoluminescence study and reactive oxygen species generation results suggested that the efficient charge carrier separation took place during the irradiation. Thus, the present work proves the ability of effective multifunctional nanomaterials to not only to degrade hazardous pollutants but also to detoxify them.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...