Protective effects of formononetin against rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury by upregulating Nrf2 in vivo and in vitro†
Abstract
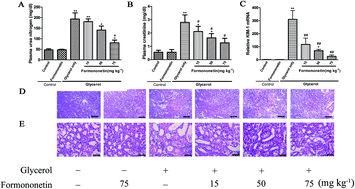
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a well-known organ injury frequently observed after rhabdomyolysis (RM). The purposes of this study are to investigate the protective effects of formononetin on RM-mediated AKI and to elucidate the involvement of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) in preventing apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. A rat model of RM was induced by an injection of glycerol. The renal histopathological changes, apoptosis of renal tubular cells and ultrastructural conditions showed significant amelioration after treatment with formononetin in rats. A formononetin dose-dependent study caused the upregulation of multidrug resistance associated proteins (MRPs) that resulted in reduced indoxyl sulfate (IS) concentrations in plasma and promoted its urinary excretion after renal injury. Formononetin increased the expression of Nrf2-mediated proteins such as BCL-XL, BCL-2 and decreased BAX, cytochrome c, caspase-9 and caspase-3 in RM-mediated AKI rats. Moreover, the changes of Nrf2 and BCL-2 family members were abrogated by Nrf2 antagonist retinoic acid (RA) formononetin-treated rats. In vitro evidence also directly demonstrated the effect of formononetin on Nrf2 and its related proteins could be reversed by brusatol (Nrf2 antagonist). In conclusion, formononetin provided renal protection due to the promotion of anti-apoptosis by Nrf2-mediated regulation of proteins.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...