Linezolid as an eradication agent against assembled methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilms†
Abstract
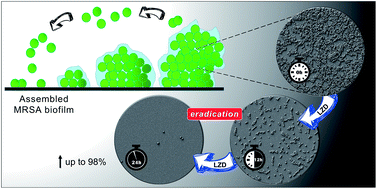
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections are a major health problem worldwide. One of the therapeutic options for treating MRSA is linezolid (LZD), which acts by binding to the ribosome bacteria and inhibiting protein synthesis. Bacterial biofilms are assembled communities which are around 10 to 1000 times more resistant to antibiotics than their planktonic counterparts. The aim of this work was to investigate the inhibition profile and the percentage of biofilm eradication in clinical and reference S. aureus strains caused by LZD. The bacterial biomass was assessed by crystal violet staining, and biofilm formation was studied using the XTT assay, with mature biofilm samples being exposed to the antibiotic and the inhibition profile also being measured by XTT. Antibiofilm activity was studied at different times by SEM to evaluate LZD eradication. All the tested strains produced a biofilm matrix, with clinical MRSA forming more biomass. The antibiofilm activity was observed at 10× MIC and revealed that LZD eliminated at least 98% of cell bunch clusters. Our results suggest that LZD is an efficient agent for eradicating MRSA biofilms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...