Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic properties of Pr2Ce2O7 nanostructures via a facile procedure
Abstract
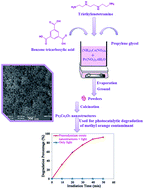
Pure praseodymium cerate (Pr2Ce2O7) nanostructures have been successfully synthesized via a facile method, utilizing Pr(NO3)3·6H2O and (NH4)2Ce(NO3)6 as precursors as well as triethylenetetramine as a new pH regulator. In this study, various complexing agents, different pH regulators and propylene glycol as an esterification agent were utilized to produce Pr2Ce2O7 nanostructures. The as-synthesized praseodymium cerate nanostructures were characterized by energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis (EDX), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), and UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. The obtained results demonstrated that the shape and particle size of the praseodymium cerate depended on the type of complexing agent and pH regulator. To compare the photocatalytic properties of the as-synthesized Pr2Ce2O7 structures, the photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange dye as a model water contaminant was performed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...