Near-infrared photoluminescence enhancement of N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC)-protected gold nanoparticles via fluorescence resonance energy transfer from NAC-stabilized CdTe quantum dots†
Abstract
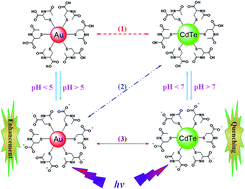
Water-soluble N-acetyl-L-cysteine-protected gold nanoparticles (NAC-AuNPs) and NAC-stabilized cadmium telluride quantum dots (NAC-CdTeQDs) have been synthesized. The near-infrared (NIR) photoluminescence (PL) of NAC-AuNPs in various aqueous pH phosphate buffers has been studied in the presence of NAC-CdTeQDs with different core sizes. The NIR PL intensities of 1.7 nm and 2.4 nm sized NAC-AuNPs increases with NAC-CdTeQDs increase. The PL enhancement for 2.4 nm NAC-AuNPs is larger than 1.7 nm NAC-AuNPs and also increases with the core size of NAC-CdTeQDs from 1.9 to 3.2 and then to 3.7 nm. In addition, the PL enhancement effect initially increases with pH and then drops with a further increase in pH, attributed to the coulombic repulsion between the same negatively charged NAC-AuNP and NAC-CdTeQD molecules at pH ≥ 7. At pH 4.0, NAC-CdTeQDs can show quenching on NAC-AuNPs. In contrast, the PL of NAC-CdTeQDs in the visible region is strongly quenched by the presence of NAC-AuNPs. The quenching efficiency decreases with the core size of NAC-AuNPs from 1.7 to 2.4 and then to 2.9 nm attributed to the decrease in the collision frequency of larger core NAC-AuNPs with NAC-CdTeQDs. Furthermore, the quenching effect increases with the decrease of pH as the coulombic repulsion between NAC-CdTeQDs and NAC-AuNPs is minimized under a low pH environment such that the intermolecular distance between the interacted NPs is shortened. The quenching of yellow and red is smaller than green NAC-CdTeQDs by NAC-AuNPs at pH 6.0 but larger than green ones at pH 7.0. The results demonstrate that the interaction between NAC-AuNPs and NAC-CdTeQD is mainly governed by the fluorescence resonance energy transfer model and the collision frequency of the AuNPs and QDs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...