Influence of shorter backbone and cholesteric monomer percentage on the phase structures and thermal-optical properties of linear siloxane tetramers containing cholesterol and benzene methyl ether groups
Abstract
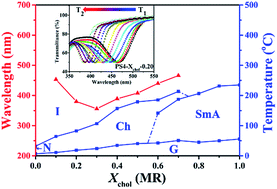
A series of new linear polysiloxane tetramers containing cholesterol and benzene methyl ether groups as side chains was successfully synthesized via a typical hydrosilylation reaction. Their chemical structures were confirmed by 1H-NMR, FT-IR and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). A combination of analysis methods such as differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), polarized optical microscopy (POM), and X-ray diffraction was carried out to systematically investigate their phase transition behaviours and phase structures. The results revealed that the mesophase structures of all the polymers were greatly dependent on the molar content of the chiral cholesteric unit (Xchol). Polymers with Xchol below 0.60 or over 0.70 could develop a stable cholesteric phase or smectic A phase, while both smectic A and cholesteric phases could be formed for polymers with Xchol between 0.60 and 0.70. Besides, polymers with Xchol below 0.60, which developed a cholesteric phase with sufficiently wide temperature ranges in the entire mesomorphic state (minimum over 50 °C and maximum over 130 °C), could also exhibit tunable selective reflection wavelengths between 470–560 nm upon heating and arbitrarily regulated glass transition temperatures between 0–40 °C. As a result, a thermochromism liquid crystalline material for temperature sensors was successfully obtained. Surprisingly, different from the results previously reported, an unusual phenomenon of the centre selective light reflection wavelength (λm) vs. Xchol, which decreased dramatically (blue shift) at first, then had a remarkable red shift with increasing Xchol, was first observed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...