The effect of temperature on the aggregation kinetics of partially bare gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
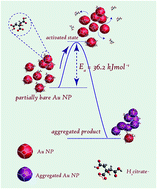
Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) without stabilizers are known to be unstable towards aggregation. Similar observations have been made with respect to the aqueous dispersion of partially bare Au NPs. Here, we report the influence of temperature on the kinetics of this aggregation process following controlled removal of the tri-sodium citrate stabilizer by dialysis. UV-visible spectroscopy was used to monitor the aggregation of the Au NPs in the temperature range of 20–60 °C. It was found that the rate of aggregation had increased with temperature. Detailed kinetic analysis showed that the aggregation process was reaction limited, demonstrating first order kinetics with an activation energy of 36.2 ± 3.0 kJ mol−1. TEM measurements confirmed the formation of aggregated structures of Au NPs with various morphologies, resulting in a varying extent of coalescence at different temperatures. During coalescence the particles either underwent oriented attachment via sharing common lattice planes or resulted in non-faceted attachment through twinning. Based on our observations a model is proposed taking into account the various probable steps involved in the formation of NP aggregates and the underlying reason towards the barrier to activation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...