Catalytic removal of organic colorants from water using some transition metal oxide nanoparticles synthesized under sunlight†
Abstract
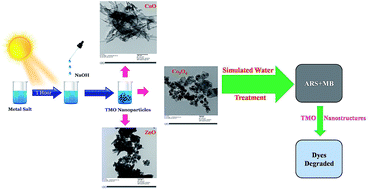
Transition metal oxides (TMO) constitute a most amazing class of materials with a wide range of properties and applications; therefore, their synthesis using a green approach is a necessity. As such, sunlight irradiation was employed to synthesize various TMO nanostructures (ZnO, CuO, Co3O4, NiO and Cr2O3) using water as a solvent. Nanoparticles obtained with distinct morphologies, such as nanotubes (ZnO; <35 nm), nanorods (CuO; 7–50 nm), nanorods, triangles and hexagons (Co3O4; 45–90 nm), needle-shaped (NiO; 2–25 nm) and nanobeads (Cr2O3; ∼17 nm) were confirmed by TEM analysis. The significance of the synthesis is in its quick approach with no thermal heat involvement, reusable catalyst, cost effectiveness and ability to fabricate almost uniformly distributed nanoparticles with small sizes. The potential of the synthesized nanoparticles was examined in the treatment of simulated water containing hazardous dyes: Alizarin Red S (ARS) + Methylene Blue (MB). Interestingly, in a short period of 180 min, 88.24% of the dye mixture was, for the most part, completely degraded using Cr2O3 nano-needles, followed by 87.96% (ZnO) > 86.86% (CuO) > 85.89% (NiO) > 80.35% (Co3O4), depending on the sizes of the respective TMO nanoparticles. This is also supported by the finding of small and non-toxic by-products such as but-2-enal, sulfur trioxide and benzoquinone. With high potential observed in the removal of dyes, TMO nanoparticles have a bright future with respect to their use as important adsorbents in waste water treatment. The advantage of the present work lies in the green synthesis of nanoparticles and their application in helping to make our environment green.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...