Nano-carbon: preparation, assessment, and applications for NH3 gas sensor and electromagnetic interference shielding†
Abstract
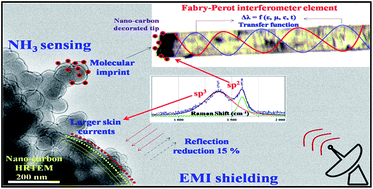
We report on the preparation and characterization of nano-carbon for applications in NH3 sensing and electromagnetic interference shielding (EMI, X-band, 8–12 GHz). Nano-carbon was synthesized by combustion of 1,7,7-trimethyl-bi-cycloheptan (camphor, C10H16O) deposited at 77 K. Morphological analysis showed nano-carbon was spherically concentric shells (40–50 nm); interconnected spatially. In Raman, vibration modes observed at 1390 (D) and 1580 (G) cm−1, indicated presence of sp3 within sp2 shells. UV-visible and photoluminescence spectroscopic analysis revealed that, band gap of nano-carbon was 4.5 eV with midgap of 2.7 eV and two flouro-excited states; making it useful for Fabry–Perot interferometer optical fibre gas sensor. Details of sensor system, its mechanism and transfer function analysis is presented. The system sensitivity was 3 ppm with response and recovery time, respectively, 5 and 8 s. The molecular imprint of NH3 on nano-carbon (1–5 ppb C-loss/10 cycles; 2 : 1, sp3 : sp2 rupture) was obtained that set life time of sensor probe. In EMI, % reflection of nano-carbon was comparable with copper. The losses due to hopping and migration current were large in nano-carbon and attributed to in-plane σ-bond and tetrahedral sites in nano-carbon that interacted with radiation at higher skin depth, around four times more than that of copper. Details of EMI shielding mechanism is presented.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...