Effect of Ce doping on the optoelectronic and sensing properties of electrospun ZnO nanofibers
Abstract
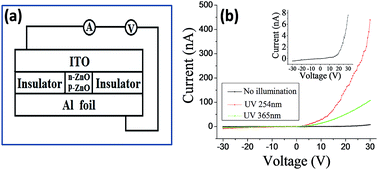
Pure n-type ZnO nanofibers and p-type Ce-doped ZnO nanofibers were prepared by electrospinning followed by calcination. Their surface morphology, elemental composition, crystal structure, and optical and electronic properties were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, and photoluminescence and UV-visible spectroscopy techniques and by their current–voltage (I–V) curves. The energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction spectra showed that Ce was successfully incorporated into the ZnO crystal lattice and that the atomic percentage of Ce to Zn was 1.46%. The photoluminescence integrated intensity ratio of the UV emission to the deep-level green emission for Ce-doped ZnO nanofibers was over twice than that of pure ZnO. The UV-visible absorption edge of the Ce-doped ZnO nanofibers red-shifted by 2.6 nm compared with the pure ZnO nanofibers. The ZnO nanofibers had a good response to ultraviolet radiation. The sensitivity (Imax/I0) of the Ce-doped ZnO nanofibers was 102, which was one order higher in magnitude than that of pure ZnO nanofibers. The field-effect curve suggested that the synthesized Ce-doped ZnO nanofibers were p-type semiconductors. A p–n homojunction device was prepared using the ZnO nanofibers and showed good rectifying behavior. The turn-on voltage reduced by about 10 V under UV irradiation. Both the ZnO nanofibers and the ZnO p–n homojunction had excellent UV sensibilities. These results suggest that Ce-doped ZnO nanofibers may have widespread applications in optical and electronic devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...