Highly selective amino-functionalized magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers: absorbents for dispersive solid phase extraction and trace level analysis of chlorophenols in seawater†
Abstract
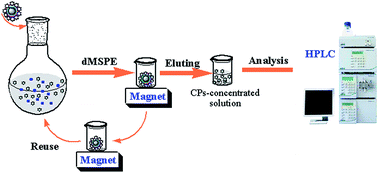
A method of dispersive magnetic solid phase extraction (dMSPE) using magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer (nFe3O4@NH2MIP) as an adsorbent coupled with high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was developed for the determination of 5 kinds of chlorophenols (CPs) in seawater samples. 8 kinds of nFe3O4@NH2MIP were synthesized via suspension polymerization by using the 5 different kinds of CPs as templates and 4 different kinds of amines for surface grafting. Compared with seven other kinds of MIP materials and the non-imprinted magnetic polymers (nFe3O4@NH2NIPs), the as-prepared nFe3O4@TEPA–PCP-MIP showed excellent extraction performance for CPs with high enrichment efficiencies, short times, high recoveries and reusabilities. Various parameters affecting the extraction efficiency of the dMSPE of the 5 target CPs were optimized, including solution pH, extraction time, desorption time, desorption solution, volume of desorption solution, kinds of absorbents, etc. The results show that under the optimal condition, linearities are obtained ranging from 1 ng L−1 to 5000 ng L−1 with correlation coefficients (R) higher than 0.9989 for the target CPs. The recoveries are between 86.5% and 98.8% at the spiked levels with the relative standard deviations (RSDs) in the range of 0.8–8.8%. The limits of detection (LODs) are in the range of 0.18–1.2 ng L−1 and the limits of quantification (LOQs) are between 0.6 ng L−1 and 4.0 ng L−1. The developed method is successfully applied for real sample analyses, which confirm that it can be applied to routine monitoring for the determination of the CPs in seawater samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...