The bio-reduction of chromate with periplasmic reductase using a novel isolated strain Pseudoalteromonas sp. CF10-13†
Abstract
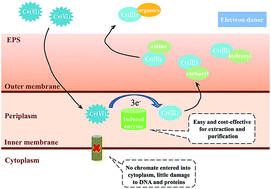
The bioremediation of Cr(VI) polluted soil and water is economical and eco-friendly compared to physical and chemical methods. However, the application of most reported bacterial Cr(VI) reduction processes could be limited by moderate/low temperatures. In this study, a marine bacterium strain, Pseudoalteromonas sp. CF10-13, with a high Cr(VI) reduction efficiency was isolated. The effects of pH, salinity, temperature and initial Cr(VI) concentration, Cr(VI) transformation, and the characterization of Cr(VI) reductase were investigated. Results showed that Cr(VI) could be almost completely reduced within 48 h at an initial concentration of <70 mg L−1, with a maximum rate of 0.86 mg g−1 h−1. A high reduction efficiency (>85%) was obtained for a wide range of temperatures (15–30 °C). It was illustrated that Cr(VI) was reduced to Cr(III), with only a small part bound to the functional groups of EPS, while most was probably soluble organic-Cr(III) in solution. Based on enzyme activity tests, the Cr(VI) reductase was a kind of inducible enzyme located in the periplasm. The activity of the Cr(VI) reductase was unaffected by ionic Cu and Pb, but inhibited by ionic Zn, Cd, and Cr(III). Sodium lactate could act as a suitable electron donor for Cr(VI) reduction through Pseudoalteromonas sp. CF10-13. Our study may provide a potential bacterial strain for application to Cr(VI) bioremediation at extended temperatures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...