Nanonization of andrographolide by a wet milling method: the effects of vitamin E TPGS and oral bioavailability enhancement†
Abstract
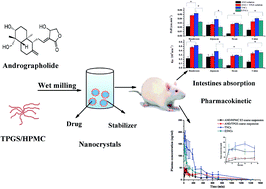
Andrographolide (AND) has wide prospects in clinical use, but suffers from the restriction of poor oral bioavailability, due to its low solubility, rapid and extensive metabolism and efflux by P-glycoprotein (P-gp). In this study, for the first time, nanocrystals of AND, a model of BCS class II, were obtained via the wet milling method, with TPGS as a stabilizer to enhance the bioavailability of AND; HPMC E5 nanocrystals (E5NCs) were fabricated as the negative control. Using the optimized formulation, AND/TPGS nanocrystals (TNCs) and E5NCs were prepared. Physical characterizations demonstrated that the two nanocrystals shared similar particle size, the same crystallinity and identical morphology. Both nanocrystals were physically stable at 4 °C and 25 °C, respectively, for at least 1 month. Significant increases in cumulative dissolution (90% and 70%) were obtained after the TNCs and E5NCs dissolved at 60 min, which were higher than for coarse AND (no more than 40%), indicating that TNCs were superior to E5NCs in dissolution. As elucidated in the single-pass intestinal perfusion studies of AND, the nanocrystals could facilitate intestinal uptake, and TPGS possessed improved intestine absorption properties. Oral administration of AND nanocrystals produced a substantial improvement in oral absorption, compared to the AND coarse suspension. Compared to E5NCs, there was a significant difference in AUC0–24h after the oral administration of TNCs. Compared to the model group, the TNCs and E5NCs inhibited xylene induced ear swelling by 59.98 and 48.06%, respectively. These results corroborated that TNCs were a promising formulation choice for the oral delivery of AND.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...