Fast response ammonia sensors based on TiO2 and NiO nanostructured bilayer thin films†
Abstract
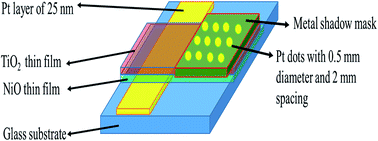
In the present work, we have synthesized TiO2 and NiO based bilayer nanostructured thin films on glass substrates via DC magnetron sputtering at room temperature. The structural and morphological properties of the bilayer samples were systematically studied using numerous analytical techniques, including X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy (AFM), field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The ammonia (NH3) gas sensing properties of both bilayer sensors towards a low detection range (5–500 ppm) within a low operating temperature regime (30–300 °C) have been extensively discussed in detail. The TiO2/NiO and NiO/TiO2 sensors exhibited high sensing responses (Rg/Ra ∼ 7.6) and (Ra/Rg ∼ 5.0) with very fast response times (∼24 s) and (∼30 s) towards 100 ppm NH3 at 280 °C and 200 °C, respectively. Furthermore, the working principle attributed behind their good gas sensing properties was also investigated via formation of p–n and n–p heterojunctions at the interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...